Introduction to Solar Off-Grid Systems
Key Takeaways
- Solar off-grid systems offer independence from the utility grid.
- These systems can significantly reduce electricity costs.
- Installation can be tailored to individual energy needs.
- Environmental benefits include reduced carbon footprint.
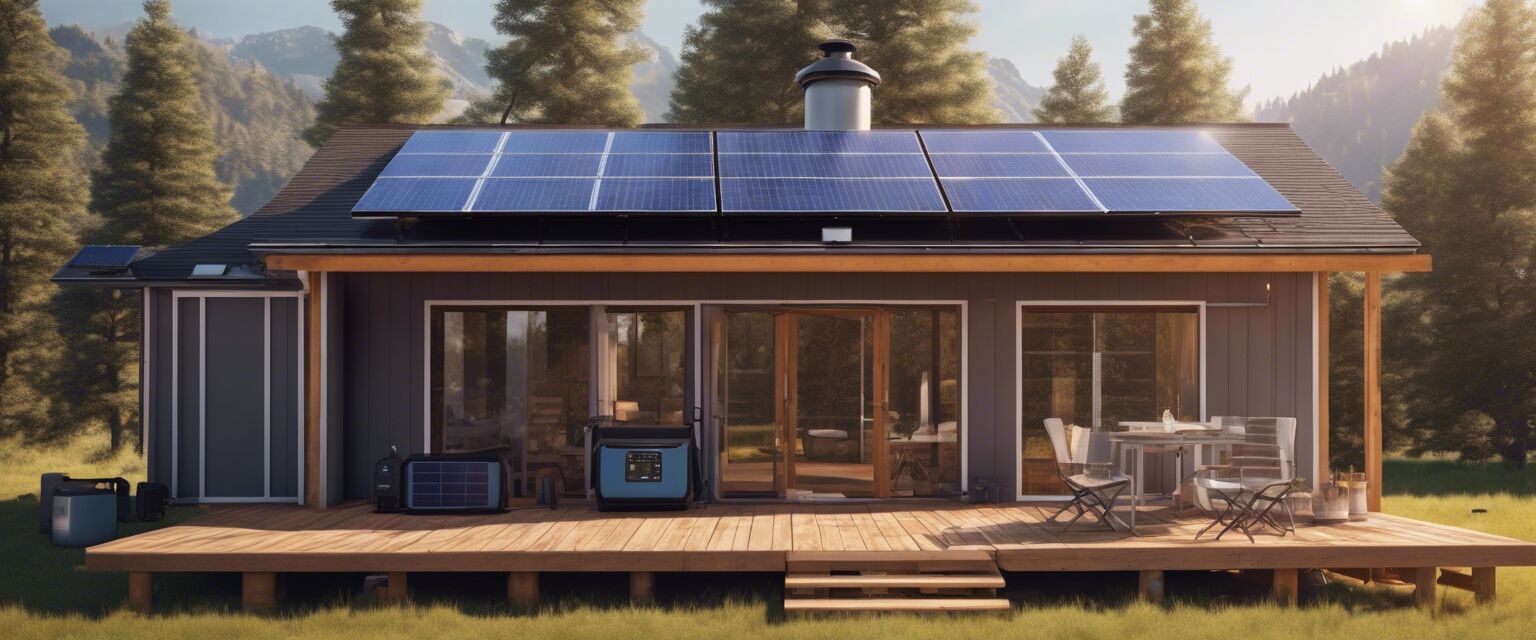
As concerns grow over power reliability and environmental sustainability, many people are turning to solar off-grid systems for their energy needs. These systems empower homeowners and businesses to generate their own electricity while minimizing their dependence on the traditional power grid. In this article, we will explore what solar off-grid systems are, their benefits, and key components to consider.
What are solar off-grid systems?
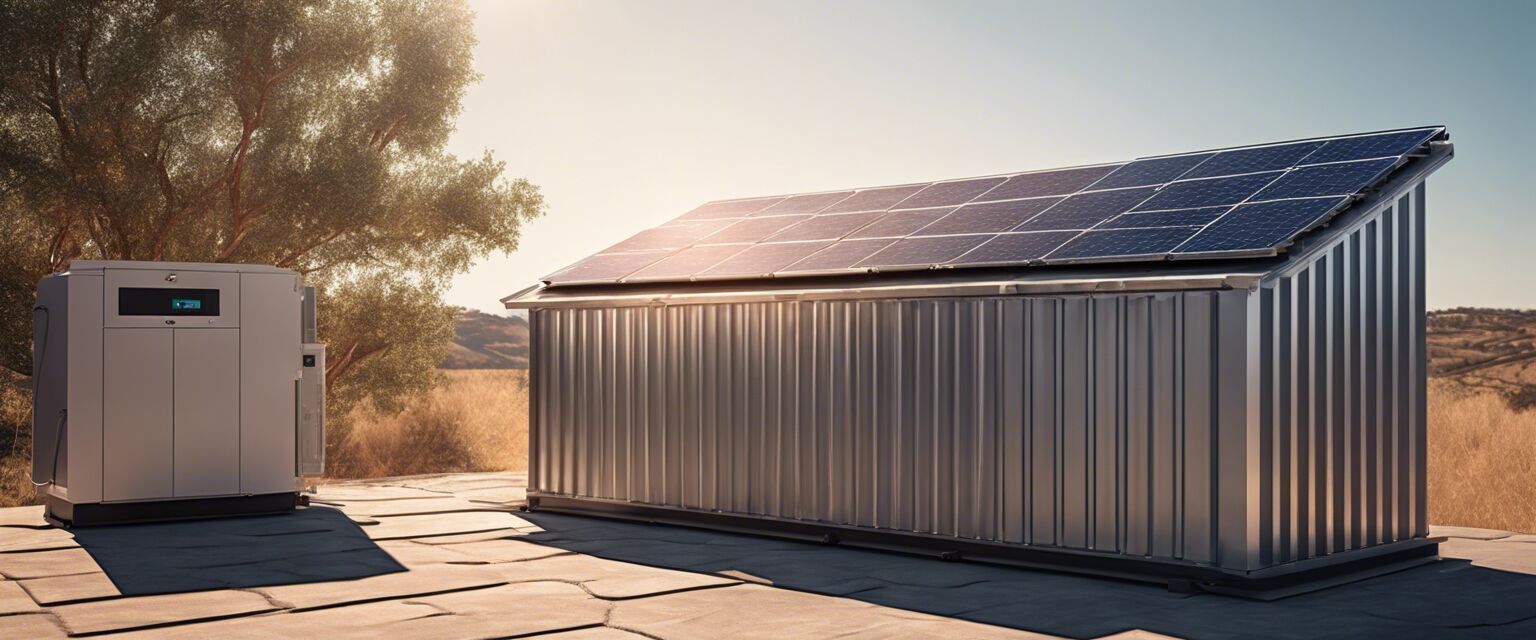
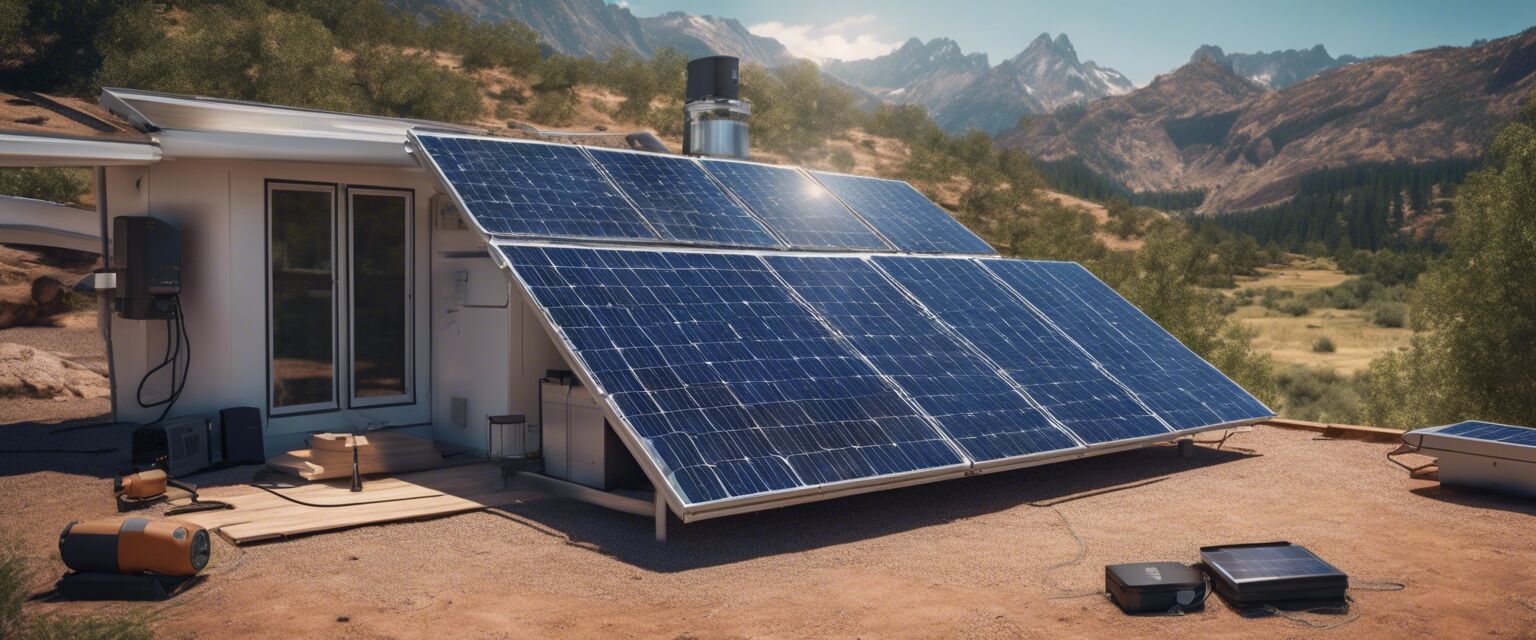
Solar off-grid systems are self-sufficient energy systems that use solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity, which is then utilized to power home appliances and devices without relying on the local utility grid. These setups typically include several key components:
- Solar panels: Convert sunlight into electricity.
- Batteries: Store electricity generated by the solar panels for use when sunlight is unavailable.
- Charge controllers: Manage the flow of electricity between solar panels and batteries.
- Power inverter: Converts stored DC power into AC power for home use.
How do solar off-grid systems work?
The process is relatively simple:
- Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it to DC electricity.
- Charge controllers regulate the flow of electricity to the batteries.
- Stored electricity is available for use at night or during cloudy days.
- The inverter converts DC electricity to AC for household devices.
Benefits of solar off-grid systems
Solar off-grid systems offer numerous advantages, making them an attractive choice for many households.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Independence | Users become less reliant on fluctuating electricity prices and power outages. |
| Cost Savings | Long-term savings on electricity bills as well as potential tax incentives. |
| Environmentally Friendly | Reduction in carbon footprint and lower greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Increased Property Value | Homes equipped with solar systems often have higher market value. |
Solar off-grid systems vs. grid-connected systems
Understanding the differences between solar off-grid and grid-connected systems can help you make an informed choice:
| Feature | Solar Off-Grid Systems | Grid-Connected Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Dependency | Independent from the grid | Depends on the utility grid |
| Energy Storage | Includes battery storage | Relies on grid power, minimal storage |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial costs, long-term savings | Lower initial costs, ongoing utility bills |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance | Minimal maintenance required |
Key components of solar off-grid systems
Investing in a solar off-grid system requires understanding its core components. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring the system's efficiency:
- Solar Panels: Available in various types like monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film.
- Batteries: Types include lead-acid and lithium-ion, each with its advantages.
- Charge Controllers: They can be PWM or MPPT, controlling energy flow effectively.
- Power Inverters: Select between pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters based on your needs.
Choosing the right solar off-grid system
When deciding on a solar off-grid system, consider the following:
Tips for beginners
- Assess your energy consumption patterns to size your system accurately.
- Consult professionals to ensure your setup meets local regulations and codes.
- Look for systems with warranties to ensure durability and reliability.
- Factor in potential future energy needs, such as electric vehicles or additional appliances.
Conclusion
Solar off-grid systems present a viable solution for those seeking independence from conventional power sources. By understanding their components, benefits, and how they operate, individuals can make informed decisions that suit their energy needs. As the technology continues to advance, the opportunity for a brighter, self-sufficient future becomes more accessible.
Pros
- Complete energy independence
- Reduction in monthly electricity bills
- Contributes to environmental sustainability
- Potential increase in home value
Cons
- High initial investment
- Requires ongoing maintenance
- Performance dependent on weather conditions
- Space required for installation
Explore more about solar systems
If you want to dive deeper into solar technology, check out our other articles: